April 29, 2019
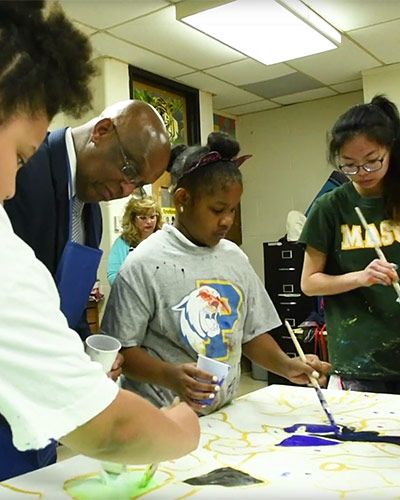

Acting Mayor Jack Young Joins Students for Reading on the Brain Art Project
Acting Baltimore City Mayor Jack Young joined 4th and 5th grade students at Callaway Elementary School to help paint a mural about the brain. It was all part of Reading on the Brain, a University of Maryland School of Medicine (UMSOM) program to teach young students about the importance of reading and how reading can stimulate brain development and inspire future success. Tracy Bale, PhD, is leading the pilot program, which also emphasizes science and helps children to understand how the brain works.
Reading on the Brain is held twice a month at Callaway Elementary. Building on the Baltimore City School’s literacy campaign, the program is promoting the benefits of reading as a means of positive brain stimulation. Studies using fMRI have demonstrated that reading stimulates mental imagery, language processing, and brain activity important in mental health and stress relief. Reading also helps the brain by building vocabulary, promoting better sleep, enhancing relationships, and improving test scores.
Acclaimed Baltimore artist Jay Wolf Schlossberg-Cohen is leading the interactive mural painting workshops, which deliver an important educational message about how reading improves brain development.
"This is really about making a difference with our kids. The idea is to have a project that will help spread the word to children and families, and we are doing it through art," says the artist. The mural will be 1800 square feet and will be hung at the school later in the year.
Professor Bale is Director of the UMSOM Center for the Epigenetic Research in Child Health and Brain Development (CERCH). The Center's mission is to facilitate translational research and community engagement important in child health and brain development, by focusing on the long-term consequences of stress and the environment on the developing brain.
About the University of Maryland School of Medicine
 Now in its third century, the University of Maryland School of Medicine was chartered in 1807 as the first public medical school in the United States. It continues today as one of the fastest growing, top-tier biomedical research enterprises in the world -- with 43 academic departments, centers, institutes, and programs; and a faculty of more than 3,000 physicians, scientists, and allied health professionals, including members of the National Academy of Medicine and the National Academy of Sciences, and a distinguished recipient of the Albert E. Lasker Award in Medical Research. With an operating budget of more than $1 billion, the School of Medicine works closely in partnership with the University of Maryland Medical Center and Medical System to provide research-intensive, academic and clinically-based care for more than 1.2 million patients each year. The School has over 2,500 students, residents, and fellows, and more than $540 million in extramural funding, with most of its academic departments highly ranked among all medical schools in the nation in research funding. As one of the seven professional schools that make up the University of Maryland, Baltimore campus, the School of Medicine has a total workforce of nearly 7,000 individuals. The combined School and Medical System (“University of Maryland Medicine”) has an annual budget of nearly $6 billion and an economic impact more than $15 billion on the state and local community. The School of Medicine faculty, which ranks as the 8th highest among public medical schools in research productivity, is an innovator in translational medicine, with 600 active patents and 24 start-up companies. The School works locally, nationally, and globally, with research and treatment facilities in 36 countries around the world. Visit medschool.umaryland.edu/
Now in its third century, the University of Maryland School of Medicine was chartered in 1807 as the first public medical school in the United States. It continues today as one of the fastest growing, top-tier biomedical research enterprises in the world -- with 43 academic departments, centers, institutes, and programs; and a faculty of more than 3,000 physicians, scientists, and allied health professionals, including members of the National Academy of Medicine and the National Academy of Sciences, and a distinguished recipient of the Albert E. Lasker Award in Medical Research. With an operating budget of more than $1 billion, the School of Medicine works closely in partnership with the University of Maryland Medical Center and Medical System to provide research-intensive, academic and clinically-based care for more than 1.2 million patients each year. The School has over 2,500 students, residents, and fellows, and more than $540 million in extramural funding, with most of its academic departments highly ranked among all medical schools in the nation in research funding. As one of the seven professional schools that make up the University of Maryland, Baltimore campus, the School of Medicine has a total workforce of nearly 7,000 individuals. The combined School and Medical System (“University of Maryland Medicine”) has an annual budget of nearly $6 billion and an economic impact more than $15 billion on the state and local community. The School of Medicine faculty, which ranks as the 8th highest among public medical schools in research productivity, is an innovator in translational medicine, with 600 active patents and 24 start-up companies. The School works locally, nationally, and globally, with research and treatment facilities in 36 countries around the world. Visit medschool.umaryland.edu/

Contact
Office of Public Affairs
655 West Baltimore Street
Bressler Research Building 14-002
Baltimore, Maryland 21201-1559
Contact Media Relations
(410) 706-5260
Related stories

Wednesday, April 02, 2025
Researchers Reveal Key Brain Differences to Explain Why Ritalin Helps Improve Focus in Some More Than Others
Nearly 16 million American adults have been diagnosed with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), but evidence suggests that more than 30 percent of them don’t respond well to stimulant medications like Ritalin and Adderall. A new clinical trial provides a surprising explanation for why this may be the case: There are individual differences in how our brains circuits are wired, including the chemical circuits responsible for memory and concentration, according to a new study co-led by the University of Maryland School of Medicine (UMSOM) and performed at the National Institutes of Health (NIH) Clinical Center.

Tuesday, April 25, 2023
Immune System Sculpts Rat Brains During Development
Researchers have established that biological sex plays a role in determining an individual’s risk of brain disorders. For example, boys are more likely to be diagnosed with behavioral conditions like autism or attention deficit disorder, whereas women are more likely to suffer from anxiety disorders, depression, or migraines. However, experts do not fully understand how sex contributes to brain development, particularly in the context of these diseases. They think, in part, it may have something to do with the differing sizes of certain brain regions.

Friday, March 31, 2023
Traumatic Brain Injury Interferes with Immune System Cells’ Recycling Process in Brain Cells
Each year about 1.5 million people in the U.S. survive a traumatic brain injury due to a fall, car accident, or a sports injury, which can cause immediate and long-term disability.

Friday, January 06, 2023
UM School of Medicine Scientists Create First Extensive Brain Cell Data Repository
Neuroscience researchers now have access to 50 million brain cells to better understand how the brain develops and functions or changes with disease or trauma. Last month, scientists at the University of Maryland School of Medicine’s (UMSOM) Institute for Genome Sciences (IGS) unveiled a “one-stop shop” for brain cell data called the Neuroscience Multi-Omic Archive (NeMO Archive). This archive is now available to neuroscience researchers to transform their understanding of the complex workings of the brain.

Monday, November 14, 2022
Brain Area Thought to Impart Consciousness, Behaves Instead Like an Internet Router
Tucked underneath the brain’s outer, wrinkly cortex is a deeply mysterious area, known as the claustrum. This region has long been known to exchange signals with much of the cortex, which is responsible for higher reasoning and complex thought. Because of the claustrum’s extensive connections, the legendary scientist Francis Crick, PhD, of DNA-discovery fame, first postulated in 2005 that the claustrum is the seat of consciousness. In other words, the region of the brain enabling awareness of the world and ourselves.

Thursday, January 27, 2022
Microbiome of Mother’s Vagina May Affect Infant Mortality Risk and Baby’s Development
A new study in mice from University of Maryland School of Medicine researchers showed that an unhealthy vaginal microbiome in pregnant mothers in combination with an unhealthy diet contributed to increased pup deaths and altered development in the surviving babies.
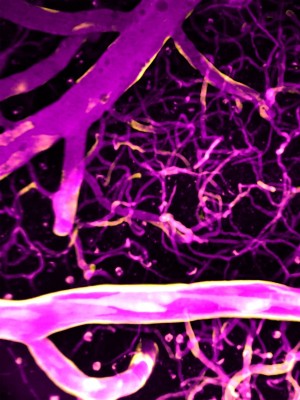
Wednesday, July 21, 2021
University of Maryland School of Medicine Study Finds Calcium Precisely Directs Blood Flow in the Brain
University of Maryland School of Medicine and University of Vermont researchers have shown how the brain communicates to blood vessels when in need of energy, and how these blood vessels respond by relaxing or constricting to direct blood flow to specific brain regions.

Wednesday, May 05, 2021
Three Leading UMSOM Faculty Named Among Maryland's Top 100 Women
The Maryland Daily Record has named three leading faculty members at the University of Maryland School of Medicine to its 2021 listing of Maryland’s Top 100 Women. The three-- Tracy L. Bale, PhD, Professor of Pharmacology; Kimberly Lumpkins, MD, MBA, Associate Professor of Surgery; and Jill RachBeisel, MD, the Dr. Irving J. Taylor Professor and Chair of Psychiatry—were chosen for their “outstanding achievements demonstrated through professional accomplishments, community leadership and mentoring,” according to the publication.
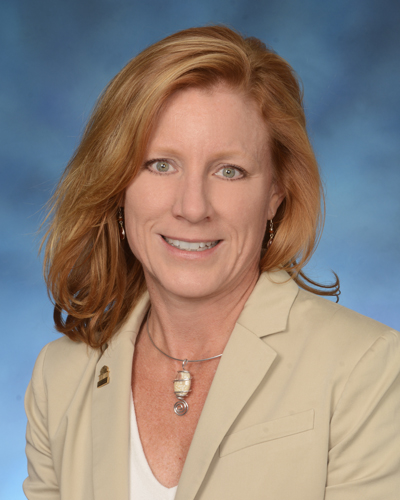

Wednesday, September 25, 2019
Dr. Tracy Bale Elected President of the International Brain Research Organization
Tracy L. Bale, PhD, Professor of Pharmacology and Director of the Center for Epigentic Research in Child Health & Brain Development has been elected President of the International Brain Research Organization.
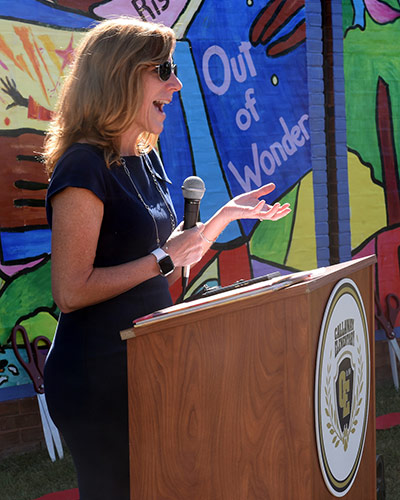

Thursday, September 19, 2019
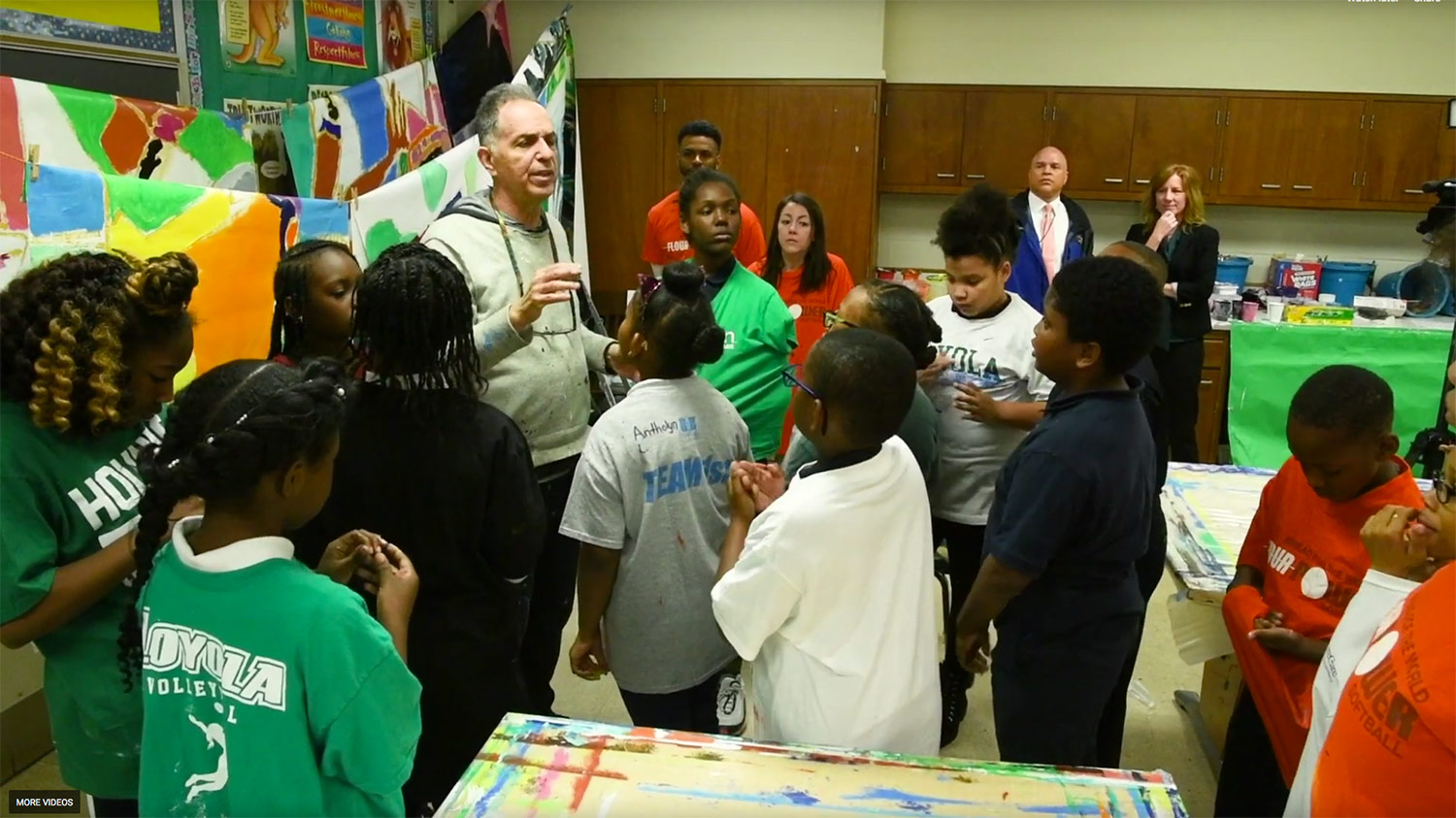
The Reading on the Brain Program Teaches Baltimore City Elementary Students About the Brain-Building Power of Reading
A giant mural with images depicting reading and the brain was unveiled during a ribbon cutting ceremony at Baltimore's Callaway Elementary School. It was part of Reading on the Brain, a University of Maryland School of Medicine (UMSOM) program to teach young students about the importance of reading and how reading can stimulate brain development and inspire future success.

Thursday, March 28, 2019
Allergic Reactions Play Role in Sexual Behavior Development in Unborn Males and Females, UMSOM Research Shows
Researchers at the University of Maryland School of Medicine and colleagues at Ohio State University have discovered that allergic reactions trigger changes in brain behavior development in unborn males and females. This latest brain development discovery will ultimately help researchers better understand how neurological conditions can differ between men and women.

Friday, March 01, 2019
UMSOM Researchers Discover Clues to Brain Differences Between Males and Females
Researchers at the University of Maryland School of Medicine have discovered a mechanism for how androgens -- male sex steroids -- sculpt brain development. The research, conducted by Margaret M. McCarthy, Ph.D., Professor of Pharmacology and Chair of the Department of Pharmacology, could ultimately help researchers understand behavioral development differences between males and females.

Monday, July 16, 2018
Microbes from Birth Canal May Affect Stress Levels of Offspring
Researchers have long known that stress during pregnancy may be transferred from the mother to her offspring. Many studies have shown that this stress can have long-lasting impacts on the physical and emotional health of the offspring. However, the mechanisms of this transfer have remained mysterious. A new study has unraveled one possible way in which these effects move from mother to child.

Wednesday, July 11, 2018
Scientists Identify Mechanism That May Explain Why Males Have a Higher Risk for Neurodevelopmental Disorders
Researchers have recently begun to realize that biological sex plays a key role in disease risk. Sex differences play a role in hypertension, diabetes, arthritis – and in many neurological and psychiatric disorders. Depression and anxiety affect females more, while neurodevelopmental disorders, including autism spectrum disorders, early onset schizophrenia, and attention deficit hyperactivity, affect more males. Males are also more sensitive to issues during pregnancy, such as maternal stress, maternal infection and exposure to drugs.

Thursday, May 03, 2018
Renowned Journalist Nicholas Kristof Speaks on Justice and Society
Renowned New York Times journalist Nicholas Kristof will speak on May 3 at the Peabody Library in Baltimore on the need to build a fairer society.

Thursday, March 01, 2018
Increased Stress on Fathers Leads to Brain Development Changes in Offspring
New research in mice has found that a father’s stress affects the brain development of his offspring. This stress changes the father’s sperm, which can then alter the brain development of the child. This new research provides a much better understanding of the key role that fathers play in the brain development of offspring.

Thursday, December 07, 2017
University of Maryland School of Medicine Scientists Identify the First Brain Cells to Respond to Sound
Some expectant parents play classical music for their unborn babies, hoping to boost their children’s cognitive capacity. While some research supports a link between prenatal sound exposure and improved brain function, scientists had not identified any structures responsible for this link in the developing brain.
