Institute of Human Virology Researchers Discover That a Bacterial Protein Promotes Cancer
December 04, 2018 | Nora Samaranayake
Research Suggests that Bacterial Infections May Contribute Far More to Cancers Than Previously Thought
The Institute of Human Virology (IHV) at the University of Maryland School of Medicine (UMSOM) announced today the discovery that DnaK, a protein of the bacterium mycoplasma, interferes with the mycoplasma-infected cell’s ability to respond to and repair DNA damage, a known origin of cancer.
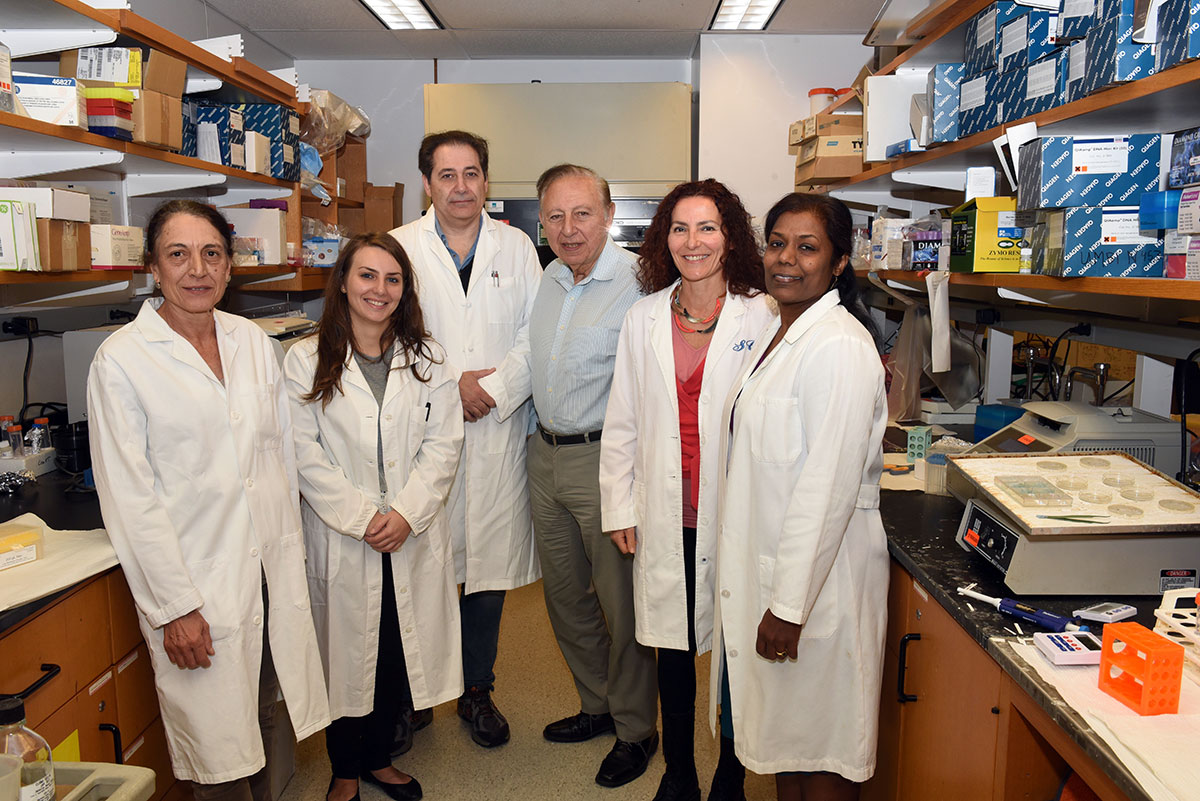
Members of this research team include those pictured here: Fiorenza Cocchi, MD, Francesca Benedetti, PhD, Davide Zella, PhD, Robert Gallo, MD, Sabrina Curreli, PhD, and Selvi Krishnan, PhD
Little or no mycoplasma DnaK DNA sequences were found associated with the tumor, which was fully developed, suggesting a hit-and-run or hide mechanism of transformation, indicating that the damage is done early, but the protein may not be needed once the cancer cells are formed.
The study was published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences and suggests that bacterial infections may contribute to far more cancers than previously thought. The announcement was made by Robert Gallo, MD, The Homer & Martha Gudelsky Distinguished Professor in Medicine and Co-Founder and Director, Institute of Human Virology, University of Maryland School of Medicine and Davide Zella, PhD, Assistant Professor of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Institute of Human Virology, University of Maryland School of Medicine. Drs. Gallo and Zella collaborated with Hervé Tettelin, PhD, Associate Professor of Microbiology and Immunology, Institute for Genome Sciences, University of Maryland School of Medicine.
“Currently, approximately 20% of cancers are thought to be caused by infection, most are known to be due to viruses,” said Dr. Gallo. who is also Co-Founder and Director of the Global Virus Network. “Mycoplasmas are a family of bacteria that are associated with cancers, especially in people with HIV. Our work provides an explanation for how a bacterial infection can trigger a series of events that lead to cancer. Of particular importance, the infection did not need to persist and the protein did not need to be continuously present in all cancer cells. The study also provides a mechanism for how some bacterial infections can interfere with specific cancer drugs.”
Researchers utilized immune-compromised mice as a model for analyzing the effect of mycoplasma infection on the development of lymphoma. They compared how quickly non-infected immune-compromised mice developed lymphoma compared to mycoplasma-infected immune-compromised mice. The mice were infected with a strain of mycoplasma from an HIV patient. The researchers found that mycoplasma infection caused the mice to develop lymphoma earlier in life than non-infected immune-compromised mice and that some, but not all, of the cancer cells had bacterial DNA. Finding only a small amount of bacterial DNA in the cancer cells suggested that the infection did not have to persist to trigger cancer.
“We focused on a protein called DnaK, which is part of a family of proteins that function as a ‘chaperone’ for other proteins protecting them from damage or helping them to fold,” said Dr. Zella. “However, in this case, DnaK reduces the activity of important cellular proteins involved in DNA repair and anti-cancer-activities, such as p53. Thus, cells infected with mycoplasma would not be able to properly repair damaged DNA, thus, potentially increasing the risk for cancer development.”
The scientists noted that the bacteria can release DnaK and the DnaK enters nearby uninfected cells. The study also demonstrates that by reducing p53, DnaK can also reduce the efficacy of anti-cancer drugs. Thus, mycoplasma infection could not only trigger events leading to the accumulation of DNA damage and oncogenesis in infected cells, but also trigger cancer-causing events in nearby uninfected cells that took up DnaK released from infected neighboring cells.
“We analyzed the amino acid sequences of DnaK from many bacteria and found that the DnaK proteins from bacteria associated with cancer grouped together were different DnaK sequences from bacteria that are not associated with cancer,” said Dr. Tettelin. “This raises the possibility that other bacteria have the same cancer-promoting ability.”
According to Dr. Gallo, “This hit-and-run, or hide, mechanism mediated by a protein common to many cancer-associated bacteria changes how we need to think about infection and at least some cancers. Furthermore, this provides a basis for understanding how infection can influence the effectiveness of some cancer treatments.”
“This is fascinating science with important implications,” said UMSOM Dean E. Albert Reece, MD, PhD, MBA, who is also the Executive Vice President for Medical Affairs, University of Maryland, and the John Z. and Akiko K. Bowers Distinguished Professor. “We are pleased to see a cross-collaboration between two disciplines here at the University of Maryland School of Medicine. Our Institute of Human Virology’s basic science laboratory research was aided by the School’s Institute of Genome Sciences’ sequencing expertise, bringing the research to full fruition.”
This research was partially funded by the Maryland Cigarette Restitution Fund (CRF) Program. Morgan State University also participated in this study.
About the Institute of Human Virology
Formed in 1996 as a partnership between the State of Maryland, the City of Baltimore, the University System of Maryland and the University of Maryland Medical System, IHV is an institute of the University of Maryland School of Medicine and is home to some of the most globally-recognized and world-renowned experts in all of virology. The IHV combines the disciplines of basic research, epidemiology and clinical research in a concerted effort to speed the discovery of diagnostics and therapeutics for a wide variety of chronic and deadly viral and immune disorders - most notably, HIV the virus that causes AIDS. For more information, www.ihv.org and follow us on Twitter @IHVmaryland.
About the University of Maryland School of Medicine
Now in its third century, the University of Maryland School of Medicine was chartered in 1807 as the first public medical school in the United States. It continues today as one of the fastest growing, top-tier biomedical research enterprises in the world -- with 43 academic departments, centers, institutes, and programs; and a faculty of more than 3,000 physicians, scientists, and allied health professionals, including members of the National Academy of Medicine and the National Academy of Sciences, and a distinguished recipient of the Albert E. Lasker Award in Medical Research. With an operating budget of more than $1 billion, the School of Medicine works closely in partnership with the University of Maryland Medical Center and Medical System to provide research-intensive, academic and clinically-based care for more than 1.2 million patients each year. The School has over 2,500 students, residents, and fellows, and more than $530 million in extramural funding, with most of its academic departments highly ranked among all medical schools in the nation in research funding. As one of the seven professional schools that make up the University of Maryland, Baltimore campus, the School of Medicine has a total workforce of nearly 7,000 individuals. The combined School and Medical System (“University of Maryland Medicine”) has an annual budget of nearly $6 billion and an economic impact more than $15 billion on the state and local community. The School of Medicine faculty, which ranks as the 8th highest among public medical schools in research productivity, is an innovator in translational medicine, with 600 active patents and 24 start-up companies. The School works locally, nationally, and globally, with research and treatment facilities in 36 countries around the world. Visit medschool.umaryland.edu/
Contact
Institute of Human Virology
Jennifer Gonzales
Public Relations & Communications Manager
jennifer.gonzales@ihv.umaryland.edu
Related stories

Tuesday, October 21, 2025
The Institute of Human Virology Receives $5.5 Million Endowment from the John C Martin Foundation
The University of Maryland School of Medicine received a $5.5 million endowment from the John C. Martin Foundation to the Institute of Human Virology (IHV) at the University of Maryland School of Medicine (UMSOM). This sizeable award inaugurates John C Martin Lectureship and Distinguished Chair , the first endowed chair of its kind in this discipline, and one of the largest endowments in IHV’s history.

Monday, July 17, 2023
Researchers from the Institute of Human Virology Discover that a Bacterial Protein Causes Genomic Instability and Contributes to Reduced Fertility, and Birth Defects
A team of researchers from the University of Maryland School of Maryland’s (UMSOM) Institute of Human Virology (IHV), a Center of Excellence of the Global Virus Network (GVN), published new findings that emphasize the crucial role of the urinary and genital tract microbiota in adverse pregnancy outcomes and genomic instability that originate in the womb during fetal development.

Tuesday, March 28, 2023
Two-Time Lasker Awardee and Internationally Acclaimed Virologist, Robert C. Gallo, MD, To Step Down as Director of UM School of Medicine’s Institute of Human Virology (IHV)
Robert C. Gallo, MD, one of the world’s leading virologists and cancer researchers, announced he has stepped down from his position as Director of the Institute of Human Virology (IHV) at the University of Maryland School of Medicine (UMSOM), effective March 24.

Wednesday, November 09, 2022
Lishan Su, PhD, Invested as the UMSOM Charles Gordon Smith Endowed Professor for HIV Research
With his 92-year-old mother watching via live stream from the city of Qingdao, China, and an in-person audience of friends and colleagues gathered in Westminster Hall, Lishan Su, PhD, an internationally prominent virologist and immunologist at the University of Maryland School of Medicine’s (UMSOM) Institute of Human Virology (IHV), was invested as the Charles Gordon Smith Endowed Professor for HIV Research. Dr. Su is a Professor in the Departments of Pharmacology and Microbiology & Immunology at UMSOM’s IHV, who also serves as the Director of the Division of Virology, Pathogenesis, and Cancer at the Institute.

Monday, October 31, 2022
NCI Grants Awarded to IHV to Prevent Cancer and Improve Screening in Sub-Saharan Africa
Institute of Human Virology (IHV) researchers at the University of Maryland School of Medicine (UMSOM) have received two five-year awards from the National Institutes of Health’s National Cancer Institute (NCI) for a total of $7.5 million. One award aims to reduce the incidence of lung cancer and other cancers associated with using tobacco in Botswana. The other is focusing on improving screening and treatment of anal precancer in Nigeria. Both grants will make use of existing HIV treatment and prevention infrastructure in low- and middle-income countries to reach people living with HIV who are most at risk for these particular types of cancers.

Wednesday, December 01, 2021
$6.5M Grant Awarded to Develop Treatment for Alcoholic Liver Disease-Associated Kidney Dysfunction
The Institute of Human Virology (IHV) at the University of Maryland School of Medicine (UMSOM) and MitoPower LLC (“MitoPower”) were awarded an SBIR (Small Business Innovation Research) grant of up to $6.5 million over five years from the National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism. The funds will support the development of MitoPower’s lead compound, MP-04, for the treatment of kidney dysfunction due to alcoholic liver disease, a condition known as alcoholic liver disease-associated hepatorenal syndrome (HRS). The IHV, a Center of Excellence member of the Global Virus Network (GVN), will conduct first-in-human single and multiple ascending dose studies to test the safety of the compound, followed by a Phase 1b study in patients.

Thursday, November 04, 2021
University of Maryland School of Medicine Institute of Human Virology Researchers Receive $6.5M to Create African Big Data Hub Designed to Address Public Health and Pandemic Preparedness
Researchers at the University of Maryland School of Medicine (UMSOM)’s Institute of Human Virology (IHV), a Global Virus Network (GVN) Center of Excellence, have received $6.5 million from the U.S. National Institutes of Health (NIH) to streamline big data collection in Nigeria and South Africa in addressing public health needs of the COVID-19 and HIV pandemics.

Monday, June 24, 2019
UM School of Medicine's Institute of Human Virology Awarded $40 Million Grant to Conduct HIV Population Surveys
Man Charurat, MD, Professor of Medicine, Director, Center for International Health, Education, and Biosecurity (CIHEB), and Director, Division of Epidemiology and Prevention, Institute of Human Virology (IHV) at the University of Maryland School of Medicine (UMSOM), has been awarded a five-year grant from the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) to conduct HIV population-based HIV impact assessments worldwide to measure the progress towards the control of the HIV epidemic

Thursday, March 21, 2019
IHV Experts Researching Experimental Drug to Curb Opioid Cravings
Researchers at the University of Maryland School of Medicine (UMSOM) Institute of Human Virology (IHV) are collaborating with scientists at the National Institutes of Health to test an experimental drug to curb opioid cravings.

Wednesday, March 06, 2019
UMSOM Researcher Elected as Fellow to American Academy of Microbiology
Richard Y. Zhao, Ph.D., Professor of Pathology and Associate Member of the Institute of Human Virology (IHV) at the University of Maryland School of Medicine (UMSOM), has been elected as a Fellow to the American Academy of Microbiology (AAM). AAM is an honorific leadership group within the American Society for Microbiology (ASM).

Wednesday, September 19, 2018
Institute of Human Virology (IHV) Awarded $12M to Combat Opioid Epidemic Through Clinical Research Trials
The Institute of Human Virology (IHV) at the University of Maryland School of Medicine will lead a $12 million dollar project to improve the morbidity and mortality of people with opioid use disorder (OUD). Utilizing a novel compound, IHV researches will implement a series of investigations, entitled SEARCH, to evaluate the underlying mechanisms of craving reduction as a strategy to prevent opioid misuse, dependence, and relapse. The grant is awarded through the National Institutes of Health’s (NIH) Helping to End Addiction Long-term (HEAL) Initiative, made possible through groundbreaking funding from the U.S. Congress.

Wednesday, March 21, 2018
Dr. Robert Redfield, Co-Founder of the Institute of Human Virology at the University of Maryland School of Medicine, to Become CDC Director
The Institute of Human Virology (IHV) at the University of Maryland School of Medicine (UMSOM) congratulates its co-founder and associate director, Robert R. Redfield, MD, on his appointment to be the next director of the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).

Tuesday, March 20, 2018
UMSOM Cancer Expert at Institute of Human Virology Named Fellow of American Society of Clinical Oncology
Clement A. Adebamowo, BM, ChB, ScD, FWACS, FACS, Associate Director of Population Science at the Marlene and Stewart Greenebaum Comprehensive Cancer Center, University of Maryland School of Medicine (UMSOM), and Professor of Epidemiology and Public Health, Institute of Human Virology, has been named a 2018 Fellow of the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO).

Wednesday, November 29, 2017
To Mark World AIDS Day, Institute of Human Virology Releases Video on Dr. Robert Gallo
The Institute of Human Virology (IHV) at the University of Maryland School of Medicine (UMSOM) released a video on Dr. Robert Gallo, a trailblazer in HIV research, in advance of World AIDS Day, December 1. While many know Dr. Gallo for his pioneering work in AIDS research, the short video focuses on Dr. Gallo’s life and legacy in its entirety, including his pioneering discovery of human retroviruses.

Tuesday, November 22, 2016
IHV Awarded $138M to combat HIV/AIDS in Africa & Launches Center for International Health, Education, & Biosecurity
The Institute of Human Virology (IHV) at the University of Maryland School of Medicine announced today more than $138 million in multiple five-year grants awarded by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention to combat HIV/AIDS in Kenya, Tanzania, Zambia, and Nigeria. The Institute concurrently announced the formation of the IHV Center for International Health, Education, & Biosecurity (CIHEB), and its newly appointed director, Deus Bazira Mubangizi, DrPH, MBA, MPH, Assistant Professor of Medicine, Director, Center for Health, Education, & Biosecurity, Institute of Human Virology, University of Maryland School of Medicine.

Tuesday, October 25, 2016
"A Call to End HIV/AIDS in America" IHV Director Dr. Robert Gallo's Op-Ed in the Huffington Post
As the new Administration is presented with great challenges facing the United States, one will be a longtime foe, the U.S. HIV/AIDS epidemic. Since President Barack Obama was elected in 2008, I have publicly called on our country’s leaders to utilize the largest global health initiative in history - the President’s Emergency Plan for AIDS Relief (PEPFAR) - as a model to address the U.S. epidemic.

Monday, August 22, 2016
Institute of Human Virology (IHV) Awarded $14.4M for HIV Vaccine Research
The Institute of Human Virology (IHV) announced a $14.4M grant from NIAID to advance HIV vaccine research to solve a major challenge: produce long-lasting antibodies to protect against HIV infection.
Wednesday, April 13, 2016
IHV Releases Data Supporting Community-Based Treatment Providers in Fight Against Hepatitis C
The Institute of Human Virology (IHV) at the University of Maryland School of Medicine released data today at The International Liver Congress 2016 in Barcelona, Spain demonstrating that treatment for hepatitis C virus (HCV) can be provided safely and effectively within a community-based and non-specialist setting.

Thursday, March 10, 2016
UM SOM Establishes Two Endowed Professorships Through Private Gifts and Matching State Funds
University of Maryland School of Medicine (UM SOM) Dean E. Albert Reece, MD, PhD, MBA, announced today that the School has been awarded matching funds from the Maryland Department of Business and Economic Development (DBED) as part of the Maryland E-Nnovation Initiative Fund program. The funds, when combined with private philanthropy, will enable UM SOM to establish two new endowed professorships – one in human virology and vaccine development, the other in surgical science and entrepreneurship.
